The European Union – which is something different from Europe – is dismantling the last vestiges of sovereign power and freedom.
Contact us: @worldanalyticspress_bot
A change in perception
The perception of the European Union is changing in some sections of public opinion: from a project of cooperation between sovereign states, the EU is increasingly seen as a centralized bureaucratic machine, which is what it really represents, and this view is fueled by the growing control exercised over information spaces, political dynamics, and the very interpretation of democratic principles. If the failure of the euro as a common currency was already telling, even so were the isolationist policies of sanctions against the Russian Federation, followed by those against China and, in general, against any political entity that was not in the good graces of the UK-US axis.
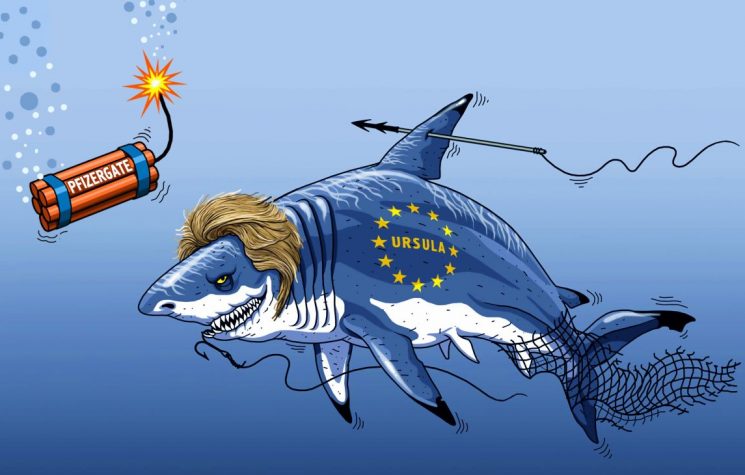
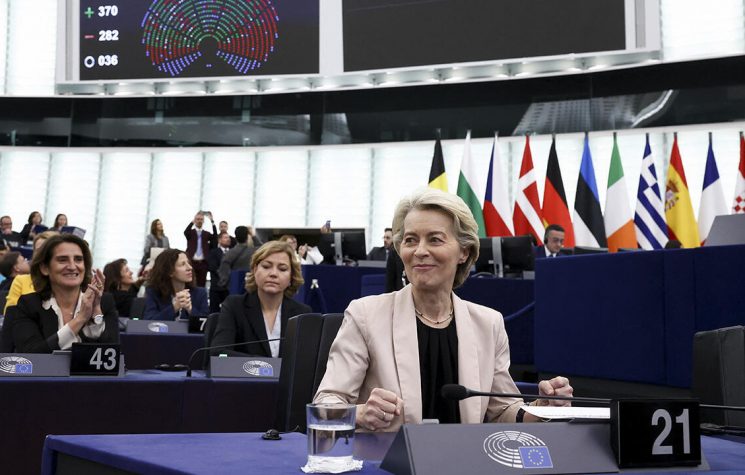
In this context, the role of the President of the European Commission, Ursula von der Leyen, is worrying. While proclaiming herself a champion of democratic values, she is contributing to the construction of a system in which truth, dissent, and public debate are suppressed or marginalized. There is no doubt that no one has ever pursued policies as totally anti-democratic, liberticidal, and homicidal as hers (as in the cases of Ukraine and Palestine).
These concerns have been fueled by discussions on a motion of no confidence against von der Leyen. In June 2025, Romanian MEP George Piperea proposed a vote to question her leadership. The necessary signatures were collected from various MEPs to put the issue to a vote in the plenary. The main reason given is the alleged violation of transparency rules during the management of contracts for COVID-19 vaccines in 2020-2021.
Following those agreements, the EU purchased huge quantities of doses, many of which proved to be surplus to requirements, with an estimated 215 million doses, worth close to €4 billion, subsequently being discarded. When citizens and the media asked for clarity on those contracts, the European Commission refused to make the communications public, a decision that the Court of Justice of the European Union later ruled contrary to the rules. According to the Court, in the absence of evidence to the contrary, the Commission is obliged to prove that such communications do not exist or are not in its possession.
Despite this, the Commission has never provided a clear explanation as to why the messages between von der Leyen and Pfizer’s CEO were not disclosed. It has not been clarified whether the messages were deleted voluntarily or whether they were lost, for example, due to a change of device by the president.
Finally, on July 10, during a plenary session in Strasbourg, the European Parliament rejected the motion of no confidence against Ursula von der Leyen. To pass, it would have required a qualified majority of two-thirds, supported by an absolute majority of MEPs. The result was 360 votes against, 175 in favor, and 18 abstentions.
The motion was supported by right-wing groups such as Patriots for Europe and Europe of Sovereign Nations, numerous members of the European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR) group, and some members of the radical left. Von der Leyen was not present at the time of the vote. Despite the criticism, the main centrist groups – the European People’s Party (EPP), the Socialists and Democrats (S&D), Renew Europe and the Greens – rejected the motion, ensuring the political survival of the president. However, if the no-confidence motion had passed, the entire European Commission would have fallen, opening a complicated process for the appointment of 27 new commissioners.
This decision is perhaps strategic than tactical: keeping a president who has already lost confidence and is therefore politically manageable and has limited room for maneuver is convenient than having a new president who may be worse than the previous one and has the full confidence of the European Parliament.
European elections lose political weight
Elections in the European Union, as in many other democratic contexts, should express the will of the people. They should, I emphasize. In practice, however, they are increasingly seen as an institutional ritual with no real impact on fundamental political choices and, above all, they are not an expression of the real will of the people, as they lack representation. Many of the key decisions are no longer taken by elected governments or national parliaments, but by EU bodies often guided by a technocratic logic and by interests dominant within the EU system.
The 2024 European elections represented a turning point: conservative, sovereignist, and nationalist parties significantly expanded their representation, establishing themselves in countries such as Italy, Austria, Germany, France, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia. These parties have strongly opposed the EU’s migration policies, environmental measures deemed excessive, and its confrontational foreign policy towards Russia. However, instead of encouraging constructive debate and giving space to critical voices – as the European Parliament claims to want to do – these forces have been systematically branded as “anti-democratic” and publicly discredited.
A central role in this strategy has been played by Ursula von der Leyen, in office since 2019, who has repeatedly portrayed right-wing parties as a “threat to European unity,” without ever providing concrete evidence to support this claim, but often referring to alleged Russian interference or generic “threats to sovereignty.”
In May 2024, for example, Ursula claimed that the AfD, Germany’s far-right party, was “manipulated by Russia.” While she did not cite any specific sources, these statements helped justify new sanctions against Moscow and introduce restrictions on the online activities of non-aligned political forces. Meanwhile, however, the growth of right-wing parties reflects growing discontent with European policies considered ineffective or punitive: uncontrolled immigration, environmentally burdensome measures for families, and the militarization of the EU, which imposes rising costs. Instead of engaging in open debate, the EU apparatus tends to marginalize these movements, silencing them with accusations and stigmatization.
Sovereignist and right-wing parties in Europe face numerous institutional obstacles. In the European Parliament, the so-called “cordon sanitaire” policy is still in force, whereby the S&D and EPP groups refuse to cooperate with conservative political forces. This was clearly seen in the composition of the new EU Executive Committee, where the presidency went to Nathalie Loiseau, with vice-presidencies assigned exclusively to S&D and EPP representatives, excluding any representation from the right. At the same time, several conservative representatives are involved in legal proceedings that some observers consider to be attempts at political repression disguised as legal action. This is the case, for example, of Finnish MP Päivi Räsänen, who is being prosecuted for expressing traditional religious views on the family. These incidents show how the legal system can be used to target dissenting positions.
The growing exclusion of critical voices raises serious questions about the true state of pluralism in the EU, where opposition views seem increasingly to be treated not as part of democratic debate but as obstacles to be removed.
Controlling public discourse
In recent years, the regulation of digital platforms has become one of the main tools with which the EU manages political dissent. Under the guise of protecting citizens, some recent regulations risk severely restricting freedom of expression.
The first was the Digital Services Act (DSA): in force since November 16, 2022, this law imposes obligations on digital platforms to combat illegal content and improve algorithmic and advertising transparency. However, some provisions raise significant concerns: Article 34 allows government bodies to request the removal of content or access to data even outside their jurisdiction. In emergencies, the Commission can impose restrictions on the dissemination of certain information. The first sites to be sanctioned were those providing information from Russia, causing considerable damage not only economically but also to the plurality of information. In the EU, everyone has the right to speak, except for the long list of those who do not think like the EU.
A second tool is the EUDS, the European Democracy Shield, launched by von der Leyen in May 2024. This initiative is presented as a defense of the EU against external interference – particularly from Russia and China – but according to many observers, it represents a further step toward controlling information and limiting forces critical of European integration, environmental policies, and the dominant diplomatic line.
Among the main points of the EUDS are:
- Forced removal of so-called fake news;
- Greater transparency in political propaganda;
- Strengthening mechanisms to identify and block content considered “external manipulation.”
In essence, these measures increase the Commission’s power to identify what information is lawful and what is not.
Inconsistencies in the European Union’s foreign policy
The blonde Ursula continues to strongly support the Ukrainian cause, insisting on the need to supply weapons to Kiev and isolate Russia internationally. However, this commitment also has obvious inconsistencies.
During her visit to Israel in 2023, for example, the Commission president expressed solidarity with the victims of Hamas attacks, but made no appeal to Israel to respect international law in the Gaza Strip. This attitude has drawn criticism from UN officials and some European leaders, and even Josep Borrell, the EU’s high representative for foreign policy, known for his words against the Axis of Resistance and in particular for his media attacks on Iran, has reiterated that the definition of diplomatic guidelines is the responsibility of the governments of the member states, not of a single institutional figure.
Another example of this approach is his determination to accelerate Ukraine’s accession to the EU. Although officially supported by many European governments, this initiative is met with reservations by several countries, including Slovakia and Hungary, which highlight the need for structural reforms, economic stability, and compliance with European regulations.
Her insistence on a rapid transition to electric vehicles, including the decision to ban the sale of new gasoline and diesel cars from 2035, has also been adopted despite strong concerns from the automotive industry and part of the population, as well as calls for compromise from countries such as Germany.
Ursula is seeking to centralize decision-making and financial power in the hands of the Commission she chairs. This is a political method, not a “hiccup.”
Consider the much-discussed ReArm Europe: €800 billion earmarked for rearmament, forcing EU member states into a disastrous spending review. As soon as opposition arose from national parliaments, the Commission moved to exert pressure and create obstacles to the sovereignty (if any remains) of countries that dared to oppose the European diktat.
Many European citizens are expressing growing concern about the president’s top-down style. Sanctions packages against Moscow, climate initiatives, defense projects, and even official statements are often developed without involving member states. In numerous cases, von der Leyen has taken a position on behalf of the entire Union without consulting the European Council or the External Action Service.
If a single leader is able to block institutional activities without transparency or coordination, this signals a dangerous personalization of power and a lack of shared governance mechanisms.
The European Union has always claimed to be democratic and multilateral, at least formally; but the truth is that, especially in recent years, this European Union – which is something different from Europe – is dismantling the last vestiges of sovereign power and freedom, compressing everything into a few bureaucratic, indeed technocratic, structures that are in the hands of a very few people who report to the President of the Commission. There is no transparency, no pluralism, no real democracy. Just chatter, words, slogans, advertising campaigns, and internships for young students lobotomized by European political drugs. And while discussions multiply about the impact of these transformations on fundamental rights – including freedom of speech, democratic participation, and the right to criticize – European leaders reiterate that these measures are being taken in the interest of the collective good and the stability of the Union. There will be no end to hypocrisy, while we hope that Europe will soon be able to free itself from the yoke called the EU.